Newest FAQs
Unlike shear plates, split rings are not made to a particular specification. Shear plates are made to a dimensional specification, ASTM D5933 and are made from a malleable casting meeting the ASTM A47 Grade 32510 specification. This is a specification that covers ferritic malleable castings intended for general use. Other products which are made to... Read more

Although these terms are used interchangeably, lags should technically be referred to as a screw and not as a bolt. A bolt is a fastener with machine thread that can accept a nut. A bolt is properly assembled and tightened by rotating the nut. A screw, on the other hand, is a fastener that is... Read more

Under the new F3125 and original A325 specification, fully threaded structural bolts are allowable if the length of the bolt does not exceed 4 times the diameter (for more information please refer to our article: What is an A325T bolt?). We recently had a customer ask about how close the threads need to be to... Read more

Portland Bolt does not have a traditional catalog or price list. The reason for this is because the majority of fasteners supplied by Portland Bolt are custom made on a per order basis. Once manufactured, the parts are shipped out immediately to the end user, so a price list would not be easy to compile. Portland... Read more
For most tie rod assemblies that Portland Bolt provides, the clevises would be forged per ASTM A668 Class A, while the turnbuckles would be manufactured per ASTM F1145 class B. ASTM A668 is a general forging specification whereas F1145 covers turnbuckles specifically. If higher strength clevises are required to develop the strength of high strength... Read more

Supplementary requirements are optional requirements within ASTM specifications that must be requested at the time of quotation or purchase to be included, otherwise the manufacturing company is not required to adhere to the supplementary requirements. ASTM specifications have varying amounts of supplementary requirements. Some specifications have as many as six or more supplementary requirements, while... Read more

Yes, there is. A193 and A320 grades B8 and B8M are assumed to be Class 1 unless otherwise specified. Class 1 fasteners are carbide solution treated, while class 2 fasteners are carbide solution treated and strain hardened. The work hardening that occurs in the manufacturing of Class 2 fasteners increases their strength. Class 2 fasteners... Read more
Portland Bolt does not manufacture or supply bolts with a Class 3A thread. Instead, Portland Bolt manufactures and supplies bolts with a Class 2A thread and nuts with a Class 2B thread. The A designates a male thread and the B designates a female thread. Essentially there are three different classes of threads, the difference... Read more
Rotational capacity testing is a test “intended to evaluate the presence of lubricant, the efficiency of lubricant, and the compatibility of assemblies.” The test is intended primarily for galvanized fasteners and fasteners that must be fully tensioned in structural applications. With A325 bolts now falling under the new F3125 specification, which covers high strength structural... Read more

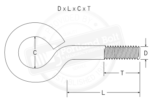
Portland Bolt manufactures eye bolts to pretty much any size imaginable. The type of eye bolt that Portland Bolt makes is not forged, but is turned and can be welded shut if needed. When load ratings are provided for eye bolts, they are normally for forged eye bolts, where the eye is formed as one solid... Read more