What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 3 Structural Bolts?
The ASTM F3125 specification covers heavy hex structural bolts including Grades A325 and A490. Both grades include Type 1 and Type 3 options.
Tension control bolts in Grades F1852 and F2280 are also available in both Type 1 and Type 3. What is the difference?
Type 3 bolts are made from weathering steel designed to eliminate the need for galvanizing, painting, or coating and provide a rust-like appearance that offers protection against the elements.
F3125 Grade A325 Type 1 structural bolts are made from medium carbon or alloy steel, while F3125 Grade A490 bolts are made from alloy steel. Plain finish Type 1 structural bolts do not provide weathering capabilities without some sort of protective coating.
What is a Type 1 structural Bolt?
Type 1 refers to an ASTM F3125 structural bolt that requires some sort of corrosion-resistant coating when exposed to the elements.
What is a Type 3 structural bolt?
A Type 3 ASTM F3125 structural bolt covers weathering steel structural fasteners. These high-strength fasteners possess atmospheric corrosion resistance and weathering properties. This means that Type 3 structural bolts are designed to weather and rust over time, but not corrode. Unlike Type 1, their rust acts as a protective barrier or “coating” that seals the bolt.
What are approved coatings for Type 1 structural bolts?
F3125 Grades A325 AND F1852 bolts can be hot-dip galvanized (ASTM F2329) or mechanically galvanized (ASTM B695 ) for corrosion resistance. The approved coatings for Grades A490 and F2280 structural bolts are zinc/aluminum corrosion protective coatings as per F3393 which is a combination of three coating standards: (ASTM F1136 Grade 3), fastener coatings with zinc-rich base coat and aluminum organic/inorganic type (ASTM F2833 Grade 1), and zinc flake coating (ASTM F3019 Grade 4). The coatings for A490 and F2280 bolts can also be applied to Grades A325 and F1852.
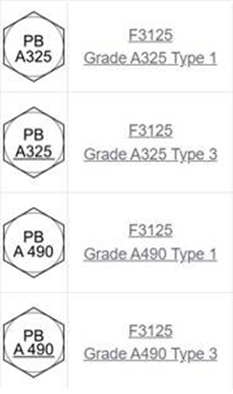
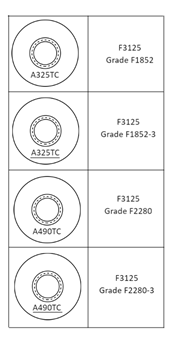
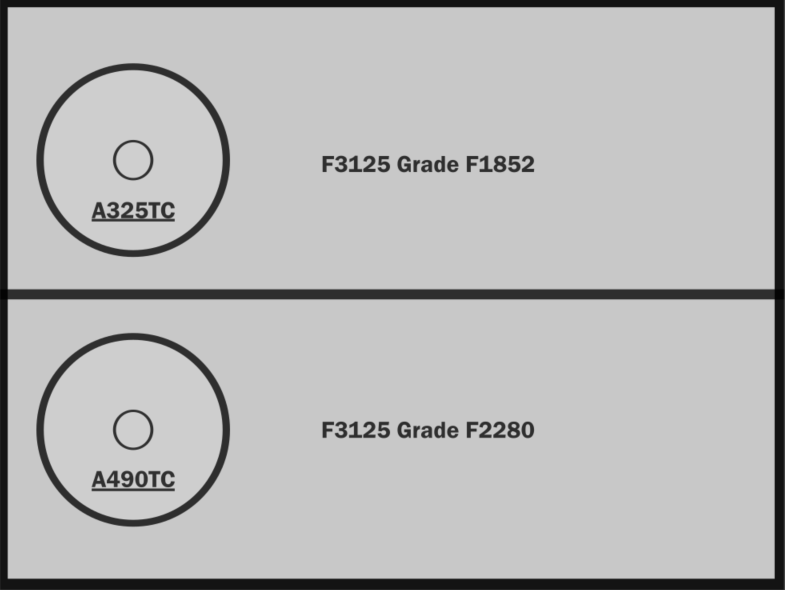
You can differentiate a type 1 and type 3 structural bolt by the head marking. As shown in the picture, a Type 3 structural bolt includes a line under the grade identification, whereas the Type 1 bolt grade is not underlined.
Compatible Nuts and Washers
The compatible nuts for A490 type 1 structural bolts and F2280 TC bolts, according to the ASTM F3125 specification, are either an A563-DH or A194-2H heavy hex nuts. The compatible washer is an F436 Type 1. For A325 Type 1 bolts and F2280 TC bolts, the same nuts and washers are compatible with the addition of an A563-C heavy hex nut when the bolt is plain finish.
For A490 Type 3 structural bolts, an A563-DH3 heavy hex nut and an F436 Type 3 washer are compatible. The same nuts and washers are compatible with an A325-3 bolt with the addition of an A563-C3 heavy hex nut.
What are the marking requirements for Type 1 and Type 3 nuts and washers?
You can verify the grade of your nuts and washers through the marking requirements per the specification. This will ensure you are pairing the correct nuts and washers with your bolts.
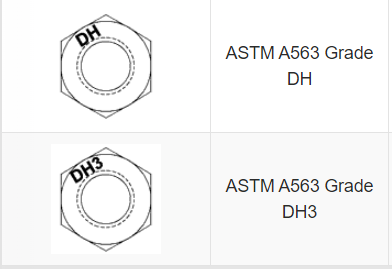
Under the A563 specification, the nuts will be identified with the grade symbol. As seen below, the Type 1 nuts are simply identified with the grade DH. The Type 3 nuts are identified with a DH3, where the 3 signifies a Type 3 weathering steel nut.

Under the F436 specification, the washers will be marked with a manufacturer’s identifier. Type 3 washers also require a symbol “3” identifying them as weathering steel. Some manufacturers will add “F436” but it is not a requirement of the specification.
When would Type 3 structural bolts be used versus Type 1 hot-dip galvanized structural bolts?
Certain weather and climate conditions can lead to issues with durability and corrosion resistance. For example, Type 3 structural bolts function best with alternating wet and dry conditions as you might experience in the Midwest, while hot-dip galvanized structural bolts are commonly used in the Pacific Northwest where the fasteners are exposed to continuous moist conditions during the fall and winter. In addition, weathering steel should not be used in a high-chlorine environment
A Type 3 structural bolt is good to use in a security solution. This would include fences, gates, and bollards. The rust layer created by the reaction of the metal to outside weathering conditions helps it blend in outdoor areas. This makes Type 3 structural bolts a good option for parks, playgrounds, farms, and vineyards.

Hot-dip galvanized Type 1 bolts perform well in salt air conditions such as coastlines, whereas Type 3 structural bolts are unable to form the protective rust layer and can pit out, causing these bolts to quickly corrode. The hot-dip galvanizing will protect the Type 1 structural bolt for many years in marine environments.
What is the availability of Type 1 and Type 3 structural bolts?
For the F3125 specification, the availability for grades A325, A490, and the type 3 versions of these grades differ.
A325 Type 1 and Type 3 structural bolts are mass-produced and readily available in diameters ½” – 1¼” in relatively short lengths. A490 Type 1 and Type 3 structural bolts are mass-produced starting at ⅝” – 1-¼”.
Since most structural bolts are very short in length, longer lengths of F3125 Grades A325 and A490 structural bolts will need to be custom manufactured, Any F3125 structural bolt with nonstandard thread lengths or head geometry are “specials” and would need to be made-to-order.
Grades F1852 and F2280 tension control bolts are mass-produced and available in similar size ranges. However, custom sizes of tension control bolts are not an option.





can ASTM type 3 bolt be galvanized?
@Emile- Yes they can, but you would then not be able to take advantage of the weathering properties of the type 3 bolt. You would end up paying considerably more for a bolt that does not perform any better from a corrosion stand point than a type 1 bolt.
With your increased warehousing capacity, are you intending to stock & sell more pre-manufactured structural bolts?
@Larry- Yes! We are working on beefing up our stock on many items, structurals among them.
Question:
Can ASTM A490 bolts be Hot Dip Galvanized?
@Farhad – No, hot dip galvanizing is currently prohibited by F3125. There are a few alternative coatings that can be applied.
does A490 type 3 can be produced with black oxide oil finish?
@Hany- most A490 type 3 bolts should come with a slightly oily, black finish. We’d be hesitant to provide a black oxide finish because that requires the addition of heat during the process. Uncontrolled heat can alter the performance of the fastener.
Lag bolts versus structural steel screws: Deck plans I am reading calls for 1/2″ dia by 5″ long lag bolts for my deck ledger board. If I were to go with structural grade screws, what size would that be?
@Paul- We are not designers, so cannot make substitution recommendations. Apologies that we cannot help.